Automated Windows Patches with Ansible
As a specialist for Linux patch management, we are often asked whether we are also familiar with Windows patch management and whether we can provide an automated solution for this.
The answer is pretty simple, YES we can. We have already built and implemented fully automated Windows patch management with Ansible for several customers.
Those who already know Ansible know that there are a lot of modules already available for Windows, which can simplify the life of a system administrator and save him from evening and weekend work.
For those of you who don’t know Ansible yet, Ansible actually comes from the Linux world and is probably one of the better known config management tools along with Puppet. Ansible is an open source tool that comes from RedHat. Since Ansible originally comes from the Linux world, it normally uses SSH as the connection method to the clients, but since not everyone wants to enable and configure SSH on their Windows host, there is also the WinRM connection method for Windows. WinRM can be run both unencrypted via http(port 5985) or encrypted via https(port 5986). In addition to basic authentication, ntlm, Kerberos, certificates and CredSSP are also available as authentication methods.
The most common requirements of our customers are actually always the same:
- Stop specific services
- Create backup or snapshot of the system
- Set downtime in monitoring
- Apply patches
- Reboot the system
- Launch services
- Test system for smooth availability
- Stop downtime in monitoring
But we can also add more steps to the process, so there is also always a request to write back the installed patches to a ticket or a file, to send certain emails or notifications, but also to create an overview of all running or not running systems.
Most customers use a WSUS server to determine in advance which server should receive which patches in the first place, but individual patches can also be selected or omitted during the update process. In general, you can filter here via update categories, but also via individual KB numbers, which updates should be searched/downloaded/installed.
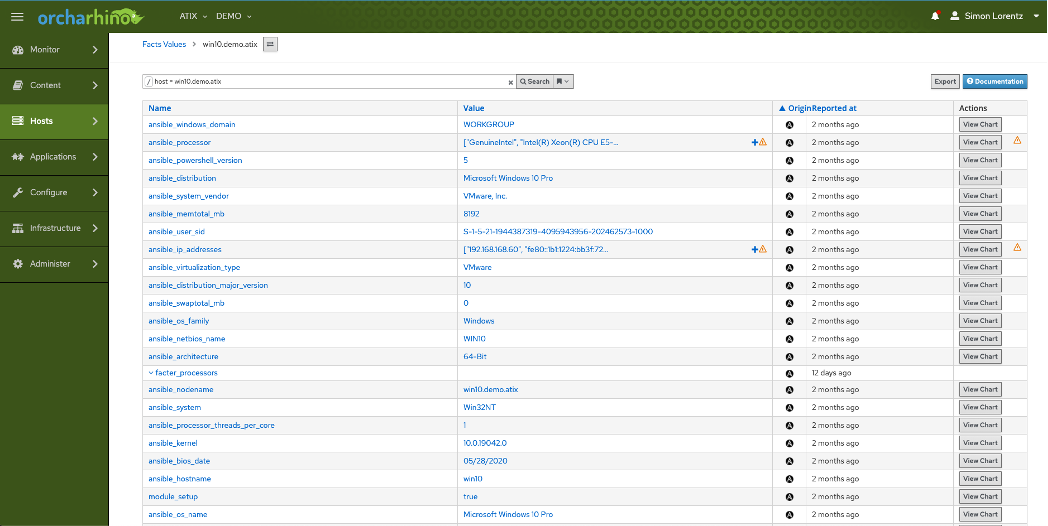
For a nicer overview of the hosts to be managed and storage of the facts collected by Ansible for a host, most customers use either our orcharhino, an AWX or a Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform as GUI and database. A small example of a facts overview in our orcharhino can be found here:
If you still have questions about rolling out Windows patches with Ansible, please feel free to contact us.
IT-Consultant at ATIX AG